In this guide, you will learn how to edit DNS records for a domain managed by Webnode and pointing to Webnode name servers (NS). Configuration is only possible for your own domain (not a project domain). You will also find information about each record type and the related values required for your domain to function correctly.
TIP: You can register your own domain or transfer it under our management. For more details, see the guides How to Register Your Own Domain and How to Transfer a Domain.
Accessing DNS record settings
1. In your project administration, open the Administration tab and select Domain management.
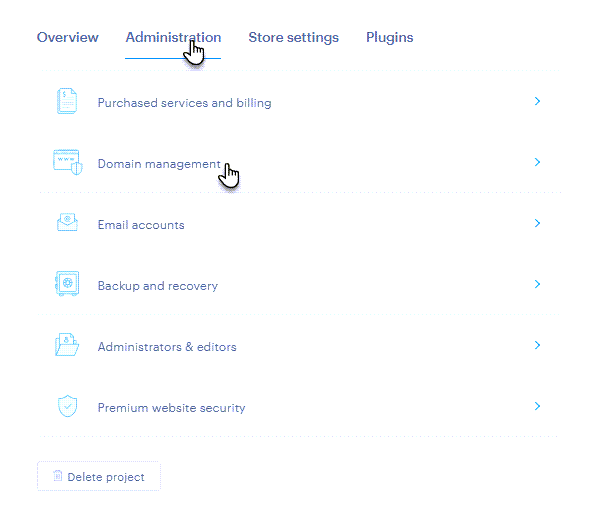
2. Click the Manage DNS button next to the desired domain.
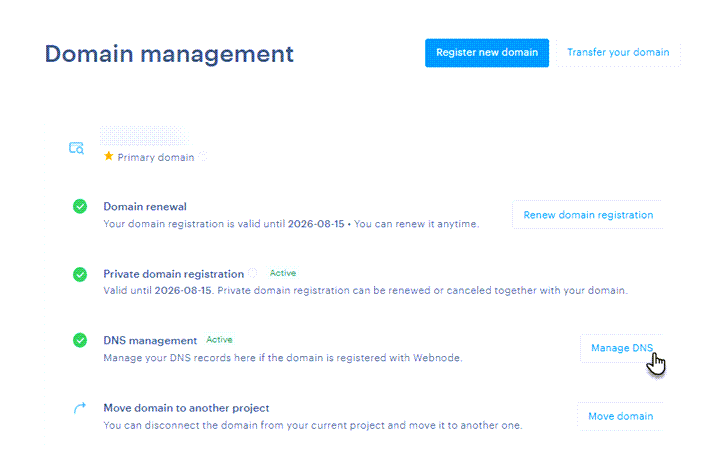
3. Here, you can Edit, Delete, or Add new records.
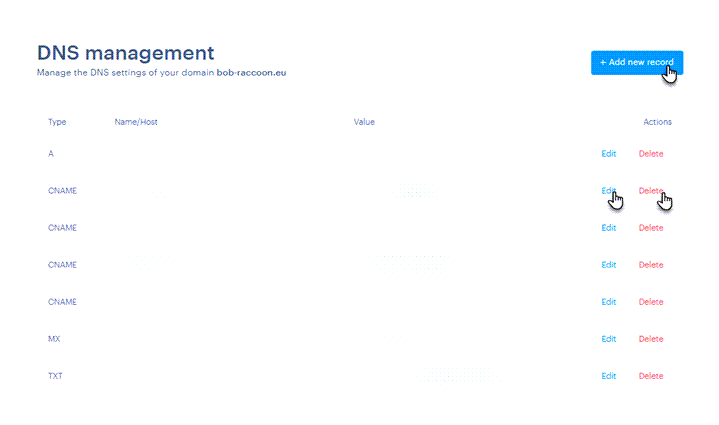
Editing existing DNS records
When editing an existing record, you cannot change its type—only its Name and Value can be modified.
WARNING: Changing existing DNS records may affect how your website functions. If you set incorrect values, your site may stop working. Webnode cannot guarantee correct functionality in such cases, so we recommend making changes only if you are an experienced user.
Simply overwrite the values and click the Save button.
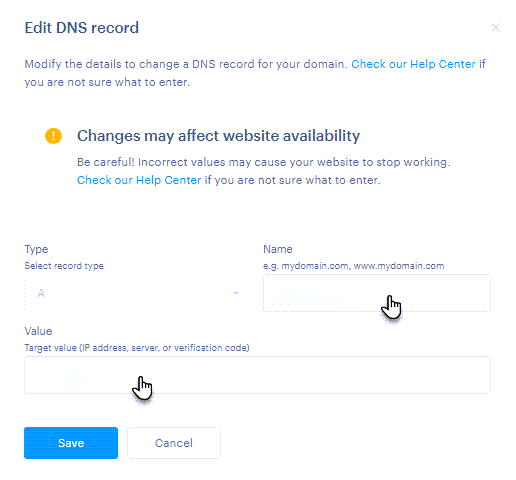
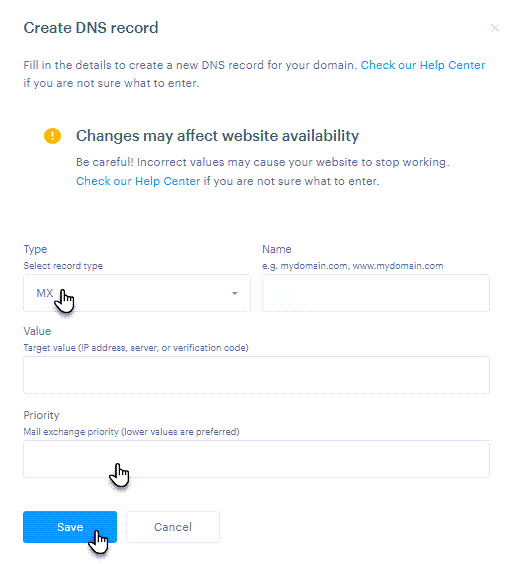
Adding a new record
Here, you can select the record type, enter the Name, and the Value. For MX records, you can also set the Priority.
• Record type specifies the kind of information the Domain Name System (DNS) stores about the domain.
• Name (also referred to as “host,” “hostname,” or “host name”) specifies which part of the domain the record applies to. For example, it can be the main domain (yourdomain.com) or a subdomain (www.yourdomain.com, mail.yourdomain.com, etc.).
• Value is the target data of the DNS record—for example, an IP address, a server name, or a verification code.
Examples of creating a record
1. You need to set an A record for the entire domain to IP 123.123.123.123 – select Type A, Name yourdomain.com, and Value: 123.123.123.123.
2. You need to add a CNAME record for the www address pointing to targetdomain.com – select Type CNAME, Name www.yourdomain.com, Value: targetdomain.com.
3. You need to create an MX record for email with priority 10 – select Type MX, Name mail.yourdomain.com, Value: mail.yourdomain.com, Priority: 10.
4. You need to add a verification TXT record for emails – select Type TXT, Name yourdomain.com, Value: v=spf1 include:spf.yourdomain.com -all.
When will the new records take effect?
After saving, the changes will propagate within 1 hour.
Record types and related values
A record
An A record maps a domain to the specific IP address of the server hosting the website. When a visitor enters the domain in their browser, the A record determines which server to connect to. This record type is essential for proper and secure website loading. When changing your hosting provider, it’s usually necessary to update the A record.
The value is a numeric IP address.
CNAME record
A CNAME record redirects one domain (or subdomain) to another domain. For example, the subdomain www.my-domain.com can be pointed to my-project.webnode.com using a CNAME record. This type of record is often used to connect a domain to third-party services such as Webnode, Google Sites, or other platforms. CNAME records simplify domain management by allowing unified target addresses.
The value is another domain.
MX record
An MX record specifies which server should receive emails sent to addresses under your domain. Correct MX record setup is required for email services to work with Webnode or external providers such as Google Workspace or Microsoft 365. Each email provider typically provides exact values you must enter. Without correctly set MX records, emails may not be delivered or may bounce back as undeliverable.
The value is the mail server’s domain name.
Priority (MX records)
Some providers may give you multiple MX records. Each MX record includes a numeric value called priority — this determines the order in which servers attempt to deliver emails. A lower number means a higher priority, so the server with the lowest value will be contacted first. If that server is unavailable, the system will try the next one with a higher priority.
If an MX record does not have a defined priority, set the value to 10.
TXT record
TXT records store text information often used to verify domain ownership or enhance email security. A common example is domain verification for services like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365. TXT records are also used for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC settings—technologies that help protect against email misuse. The values for these records are typically provided by the service you are using.
The value is a text string.
Other records and subdomains
If you need to modify other types of records not listed in the administration or if you want to create a new subdomain from your own domain (for example, shop.yourdomain.com) please contact our customer support.











